| 水泥路面接缝传力杆周围混凝土损伤塑性分析 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 周正峰, 罗君豪, 康玉峰. 水泥路面接缝传力杆周围混凝土损伤塑性分析[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2022, 22(4): 117-127. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2022.04.008 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 周正峰 罗君豪 康玉峰 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.西南交通大学 土木工程学院,四川 成都 610031;;2.西南交通大学 道路工程四川省重点实验室,四川 成都 610031 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金项目51878575 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 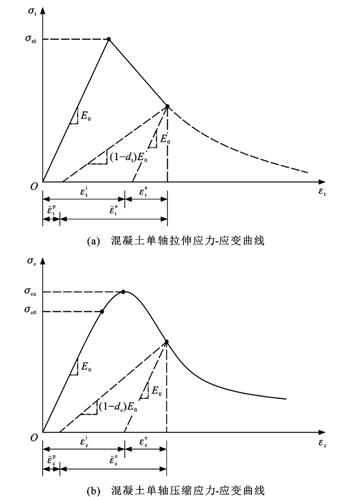
为揭示水泥路面接缝传力杆周围混凝土的受力特性与损伤机理,基于ABAQUS有限元软件,介绍了混凝土损伤塑性(CDP)模型及其参数确定方法,应用CDP模型模拟了混凝土试件单轴拉伸和压缩试验,通过对比模型试验结果验证了CDP模型参数的准确性;在此基础上,建立了接缝设置传力杆的水泥路面三维有限元模型,分析了在不同轴载作用下水泥路面接缝传力杆周围混凝土的塑性应变、损伤因子和等效应力的分布和发展规律,对比了采用CDP模型与混凝土弹性模型时传力杆周围混凝土的应力差异。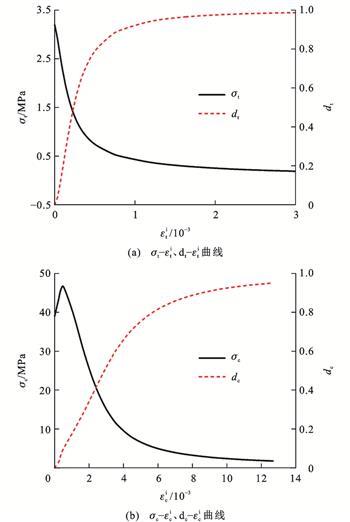
分析结果表明:对于混凝土单轴拉伸、压缩试件,基于CDP模型的应力-变形全曲线模拟结果均与试验结果一致,说明CDP模型及其参数确定方法准确;对于接缝设传力杆的水泥路面,当荷载作用在接缝传力杆黏结端上方板边时,传力杆黏结端混凝土的受力最为不利;随着轴载的增大,传力杆黏结端底部混凝土率先发生损伤塑性,等效应力逐渐减小;当轴载从100 kN增大至250 kN时,传力杆周围混凝土塑性区范围从底部135°~225°扩展至60°~300°,底部150°~210°范围内混凝土发生完全损伤塑性而退出工作,等效应力趋于0,应力重分布导致更多的荷载由传力杆两侧和上部混凝土承担;若传力杆周围混凝土采用弹性模型,传力杆底部混凝土等效应力将不断增大而超过极限强度,因此,分析传力杆周围混凝土应力集中问题建议采用CDP模型。

|
| 关 键 词: | 路面工程 水泥路面 混凝土损伤塑性 接缝 传力杆 |
| 收稿时间: | 2022-02-22 |
|
| 点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



