| 高速动车组转向架端部悬挂件对构架应力的影响 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 杨广雪, 李爽, 张子璠, 李秋泽, 谌亮. 高速动车组转向架端部悬挂件对构架应力的影响[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(3): 300-310. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.03.022 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 杨广雪 李爽 张子璠 李秋泽 谌亮 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.北京交通大学 机械与电子控制工程学院,北京 100044;;2.中车青岛四方机车车辆股份有限公司,山东 青岛 266111;;3.中车长春轨道客车股份有限公司,吉林 长春 130062 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金项目12072020 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 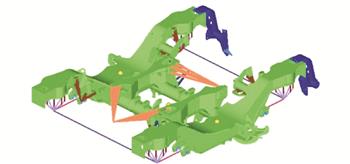
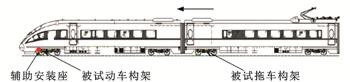
为了探究高速动车组转向架端部悬挂件对构架应力的影响规律,依据UIC 615-4标准,对转向架构架与端部悬挂件进行了有限元仿真,校核了构架疲劳强度;开展了实际运营条件下的跟踪测试试验,分析了不同位置测点应力的时、频域特征,计算了等效损伤;结合模态计算探讨了转向架端部悬挂件对构架侧梁端部应力状态产生较大影响的成因。分析结果表明:依据标准计算的弹簧帽筒区域的疲劳强度满足要求;远离辅助安装座区域的弹簧帽筒测点,实测最大等效损伤为0.01,靠近辅助安装座区域的弹簧帽筒测点,实测最大等效损伤为0.45,明显高于远离辅助安装座区域的测点;对于靠近辅助安装座区域的弹簧帽筒测点中,弹簧帽筒外侧测点即更靠近辅助安装座区域测点的等效损伤均高于内侧测点,二者等效损伤最大相差84.16%;实测数据存在38 Hz的主频,与辅助安装座和构架连接整体的第4阶模态接近,结合实测数据时频分析结果证明,车辆行驶与轨道不平顺波长共同作用产生的激扰,激起了辅助安装座和构架连接整体的第4阶模态,发生P2共振导致弹簧帽筒区域产生过大应力。
|
| 关 键 词: | 高速动车组 转向架构架 辅助安装座 有限元分析 频域分析 短时傅里叶变换 共振 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-01-07 |
| 本文献已被 CNKI 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|


