| 三维水翼云空泡非定常特性数值分析及试验验证 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 何朋朋, 李子如, 张孝旺, 等. 亚格子模型对三维扭曲水翼空化现象的影响[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2022, 17(3): 187–195. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.02387 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 何朋朋 李子如 张孝旺 贺伟 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.武汉理工大学 高性能舰船技术教育部重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430063;2.武汉理工大学 船海与能源动力工程学院,湖北 武汉 430063 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金资助(215202001,2019III076GX);国家自然科学基金重点国际合作研究项目资助(51720105011);领域基金重点课题资助(61402070105) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 
目的 旨在探究三维扭曲水翼空化数值模拟中网格密度及亚格子模型的适应性问题。 方法 为此,使用大涡模拟(LES)方法和Schnerr-Sauer(S-S)空化模型对Delft Twist11N三维扭曲水翼的非定常空化流场进行数值模拟,重点研究3套不同密度的网格和WMLES,SL,WALE这3种亚格子模型对Delft Twist11N水翼空化演变过程、空化脱落频率及时均升阻力系数等的影响。 结果 结果表明:适当的网格加密形式既能够捕捉到较多的细小空泡脱落、马蹄形云空泡的初生与溃灭等非定常空化演变现象,又能够获得具有较高精度的空泡脱落频率、时均升阻力系数和时均压力分布。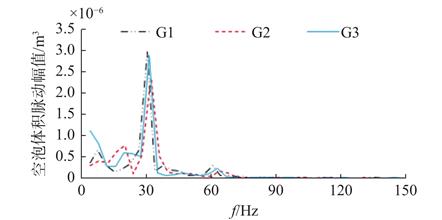
相较于WMLES和SL亚格子模型, WALE亚格子模型较好地捕捉到了片空泡及云空泡的演变,在预报空泡脱落频率、时均升阻力系数及压力系数方面精度较优。 结论 因此,推荐采用基于WALE亚格子模型的LES方法进行非定常云状空化的数值模拟。

|
| 关 键 词: | 三维扭曲水翼 云状空泡 大涡模拟 亚格子模型 网格密度 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-05-24 |
| 修稿时间: | 2022-03-03 |
|
| 点击此处可从《中国舰船研究》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《中国舰船研究》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



