| 悬架馈能作动器力学特性测试及非线性主动控制器设计 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 陈士安, 管毓亮, 任洁雨, 姚明, 蒋栋. 悬架馈能作动器力学特性测试及非线性主动控制器设计[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2022, 22(4): 232-243. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2022.04.018 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 陈士安 管毓亮 任洁雨 姚明 蒋栋 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.江苏大学 汽车与交通工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013;2.浙江万向马瑞利减震器有限公司,浙江 杭州 311215 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金项目52575239国家自然科学基金项目52072158 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 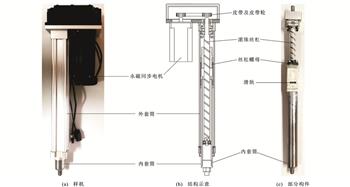
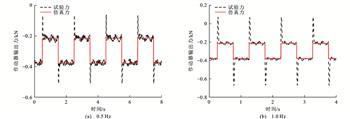
为提高车辆的乘坐舒适性并兼具回收振动能量的功能,对试制PMSM-滚珠丝杠式馈能作动器进行了力学特性测试,对库仑阻尼和作动器等效惯性质量进行识别,根据识别结果设计了馈能型主动悬架非线性控制器;结合电磁动力学建模、电气参数校核,采用分级变压充电试验方法对作动器样机进行三角波及正弦波位移输入下的力学特性测试,利用参数拟合使建模仿真力学特性曲线逼近实测曲线,完成库仑阻尼识别和等效惯性质量验证;对含有库仑阻尼及作动器等效惯性质量的主动悬架力学模型中的非线性项进行前馈反馈线性化处理,并对簧载质量/非簧载质量加速度项正则化处理,在此基础上根据作动器最大输出力设计了双约束H2/H∞控制器;利用数值仿真对被动悬架、理想主动悬架、常规H2/H∞控制主动悬架和双约束H2/H∞控制主动悬架进行悬架综合性能对比验证及馈能性能分析。
分析结果表明:双约束H2/H∞控制主动悬架的簧载质量加速度均方根和综合性能指标较被动悬架分别降低47.05%和51.67%,仅比理想主动悬架分别差1.86%和1.34%,且比常规H2/H∞控制主动悬架分别优19.28%和11.21%;库仑阻尼和电机定子电阻分别消耗掉了作动器总吸收功率的18.99%和20.19%,相比之下,流向蓄电池的回收平均功率高达60.82%。
|
| 关 键 词: | 车辆工程 主动悬架 馈能作动器 力学特性测试 参数识别 非线性双约束H2/H∞控制 |
| 收稿时间: | 2022-02-02 |
|
| 点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



