| 基于柔性多体动力学的地铁车辆半主动控制 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 陈兆玮, 朱国. 基于柔性多体动力学的地铁车辆半主动控制[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(6): 298-309. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.06.024 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 陈兆玮 朱国 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.重庆交通大学 机电与车辆工程学院,重庆 400074;;2.重庆交通大学 城市轨道交通车辆系统集成与控制重庆市重点实验室,重庆 400074 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金项目52008067中国博士后科学基金项目2019M650236重庆市基础研究与前沿探索项目cstc2018jcyjAX0271省部共建山区桥梁及隧道工程国家重点实验室开放基金项目SKLBT-19-002 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 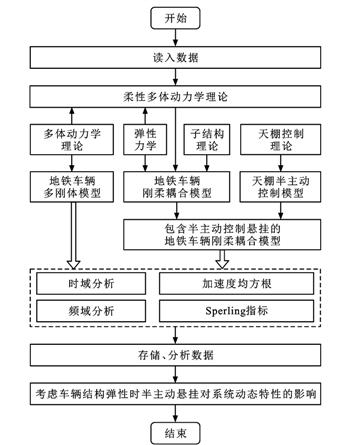
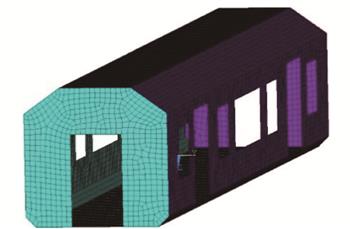
为了对地铁车辆的运行性能实现更准确的评估和更有效的优化,借助有限元理论和子结构理论建立了车体和转向架构架等关键零部件的柔性动力学模型;基于天棚半主动控制算法和柔性多体动力学理论,建立了考虑半主动控制悬挂的地铁车辆刚柔耦合动力学模型;考虑轨道随机不平顺的影响,研究了半主动控制悬挂以及结构柔性对地铁车辆运行稳定性和乘坐舒适性的影响。研究结果表明:相对于传统的悬挂装置,天棚半主动控制极大降低了车辆的振动加速度,并使其变化趋势更加平缓,对车辆的低频振动有明显的抑制作用;采用本文的研究参数,天棚半主动控制在直线段可使车辆的垂向Sperling指标和垂向振动加速度均方根(RMS)分别降低26.8%和7.5%,使车体横向Sperling指标和横向振动加速度RMS分别降低8.8%和4.9%,而在曲线段,天棚半主动控制可使车辆垂向Sperling指标和垂向振动加速度RMS分别降低25.1%和5.7%,使横向Sperling指标和横向振动加速度RMS分别降低15.6%和8.3%,车辆的乘坐舒适性和运行稳定性大幅提升;考虑结构柔性时,车辆的垂向Sperling指标和垂向振动加速度RMS相比于未考虑结构柔性时分别增大了4.3%和6.8%,横向Sperling指标和横向振动加速度RMS分别增大了3.0%和3.4%。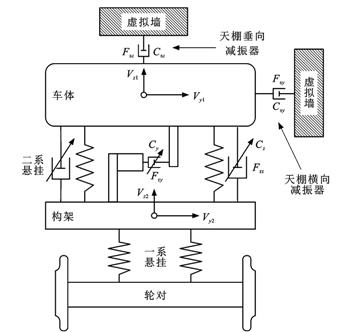
可见,车体和构架的结构柔性对车辆的动态特性有较大影响,在对车辆运行稳定性和乘坐舒适性进行计算和评估时不可忽略。
|
| 关 键 词: | 轨道车辆 柔性多体动力学 半主动控制 子结构理论 有限元理论 动态特性 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-07-08 |
| 本文献已被 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



