| 轨道交通永磁同步牵引系统发展概况与关键技术综述 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 张济民, 苏辉, 任乔, 李伟, 周和超. 轨道交通永磁同步牵引系统发展概况与关键技术综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(6): 63-77. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2021.06.005 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 张济民 苏辉 任乔 李伟 周和超 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 同济大学 铁道与城市轨道交通研究院,上海 201804 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家重点研发计划2018YFB1201603-08国家自然科学基金项目51805374 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 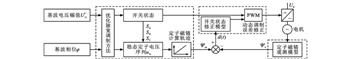
为系统分析和总结轨道车辆永磁牵引系统控制技术研究与发展趋势,介绍了永磁同步电机作为牵引电机应用于轨道交通领域的优缺点和国内外永磁同步牵引系统的应用情况;回顾了大功率牵引逆变器在低开关频率下的控制技术和永磁同步电机牵引控制技术,分析了脉宽调制策略、弱磁控制等关键技术的设计思想、研究方法等;总结了近几年国内外研究成果,讨论了各类控制方法的优点和局限,并展望了永磁同步电机在轨道交通牵引领域的发展前景和面对的挑战。
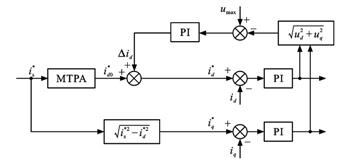
研究结果表明:内置式永磁同步电机适用于直驱系统,具有体积小、效率高等优势;牵引逆变器通常采用混合脉宽调制策略,低频段采用异步调制,中频段为同步调制,方波工况下采用单脉冲调制,其中特殊同步调制下系统动态性能的提升和不同调制方法之间的平滑切换是牵引逆变器脉宽调制技术的难点;电机控制策略主要针对基于双电流调节器、电压矢量角弱磁控制和方波工况下弱磁控制这3种高速运行区的弱磁控制方法进行研究;在前期研究的基础上,应进一步考虑永磁同步电机的无位置传感器技术、故障在线诊断与预测和高精度参数辨识问题;牵引传动系统的机电耦合特性和短路故障处理是今后重点关注的研究方向。
|
| 关 键 词: | 车辆工程 永磁同步电机 轨道交通 牵引系统 脉宽调制策略 弱磁控制 |
| 收稿时间: | 2021-05-29 |
| 本文献已被 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



