| 基于交通流生存函数的交叉口通行能力计算模型 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 胡尧, 韦维, 商明菊, 李丽, 李扬. 基于交通流生存函数的交叉口通行能力计算模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2019, 19(4): 137-150. doi: 10.19818/j.cnki.1671-1637.2019.04.013 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 胡尧 韦维 商明菊 李丽 李扬 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.贵州大学 数学与统计学院, 贵州 贵阳 550025;;2.贵州大学 贵州省公共大数据重点实验室, 贵州 贵阳 550025;;3.贵州民族大学 数据科学与信息工程学院, 贵州 贵阳 550025 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金项目11661018贵州省科技计划项目黔科合平台人才[2017]5788号全国统计科学研究项目2014LZ46贵州省科学技术基金项目黔科合J字[2014]2058号 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 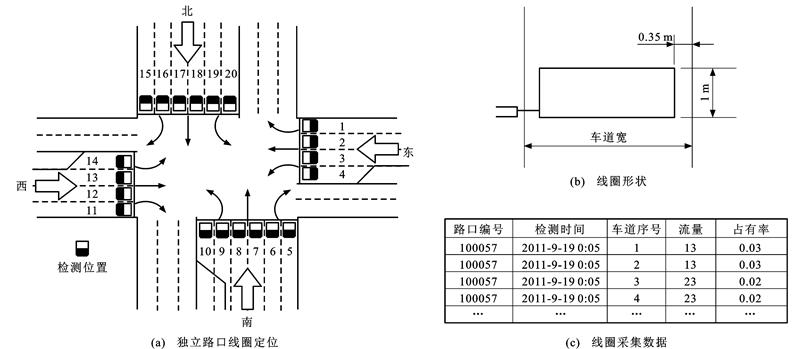
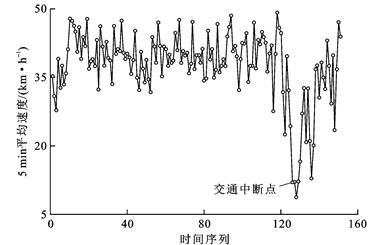
针对基本通行能力不能全面反映道路交通状况的缺点, 提出了城市道路随机化通行能力概念; 依据评价体系定义交通中断与持续中断, 量化了城市道路交通拥堵程度; 研究了现有通行能力估计方法, 利用乘积限与寿命分布列构造并估计了交通流分布函数; 结合交叉口各入口交通流数据特性改进传统连续交通流参数模型, 提出了基于交通流生存函数的交叉口通行能力计算模型; 将该模型估计结果与道路通行能力手册HCM2010中的模型估计结果和交叉口实测流量进行误差对比。分析结果表明: 生存函数模型计算出的中断、持续中断交叉口通行能力与HCM2010中的模型计算结果误差均值分别为0.162 1与0.116 4, 方差分别为0.029 0与0.015 2, 两者误差波动均较小; 提出的计算模型结果与实测较大流量相对误差分别为9.720%、3.822%和4.936%、4.779%, 统计意义下提出的计算模型相对误差为5.871%, 估计效果稳健; 城市道路交通中断次数、可接受中断概率、交通流、速度与道路通行能力之间存在生存函数乘积限对应关系, 研究交叉口的通行能力为7 632 pcu·h-1, 提出的计算模型估计结果更具有可靠性。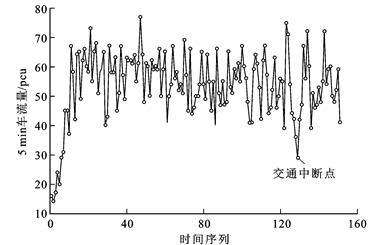
可见, 提出的计算模型适用性较好, 特别在不同拥堵程度的城市道路交通区域, 通过可接受中断概率估计通行能力, 可为城市道路交通组织与管理部门提供优化目标、科学决策和易于接受的理论依据。
|
| 关 键 词: | 通行能力 生存函数 交通流 乘积限 交通中断 |
| 收稿时间: | 2019-03-18 |
| 本文献已被 CNKI 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《交通运输工程学报》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



